The Road Construction Process: A Step-by-Step Journey
Roads connect cities, villages, and people. They help transport goods and services. A well-built road improves travel and boosts the economy. But how is a road built? Let’s explore the full process in simple steps.
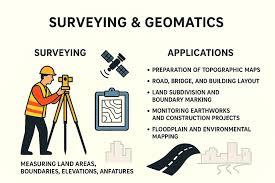
1. Planning and Surveying
The first step is planning. Engineers study the area. They check the soil, land type, and traffic needs. A survey team uses tools like GPS and drones. They mark the road path. This helps avoid hills, rivers, and buildings.
Government approvals are needed. Forest clearance and land rights must be secured. As per recent updates, 90% of land must be acquired before work begins.

2. Design and Budgeting
Next comes designing. Experts prepare maps and drawings. These show road width, curves, and drainage. Bridges and tunnels are also planned.
The budget is prepared. It includes cost of materials, labor, and machines. The government or private companies approve the funds.
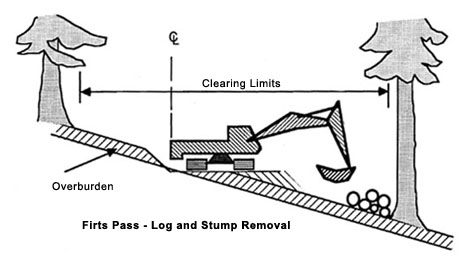
3. Clearing the Site
The construction team clears the land. Trees, rocks, and old structures are removed. Bulldozers and excavators are used. Safety measures are followed to protect workers and nearby homes.
4. Earthwork and Grading
This step shapes the road. Soil is dug and leveled. Hills are cut and low areas are filled. Rollers press the soil to make it firm. This base must be strong to hold heavy traffic.
Drainage systems are built. These prevent water from damaging the road.
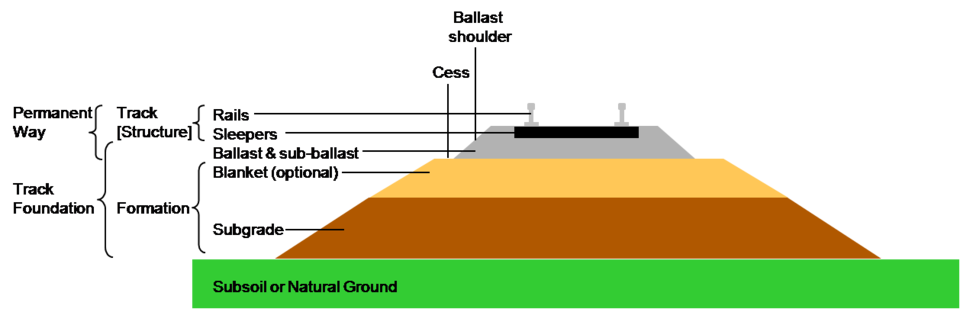
5. Laying the Foundation
The foundation is called the sub-base. It is made of crushed stones and gravel. This layer supports the road surface. It is spread evenly and compacted.
Sometimes, a layer of sand or geotextile is added. This improves strength and prevents erosion.

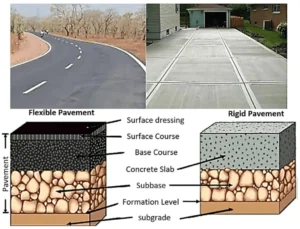
6. Paving the Road
Now the road gets its top layer. Asphalt or concrete is used. Asphalt is black and flexible. Concrete is grey and strong.
Machines heat and spread the material. Workers smooth it with rollers. This layer must be even and thick.
In cities, concrete roads are common. On highways, asphalt is preferred.

7. Finishing Touches
Road signs, lights, and markings are added. Footpaths and dividers are built. Safety rails are installed on bridges and curves.
Green belts and trees may be planted. This makes the road look better and reduces pollution.
8. Quality Checks and Opening
Engineers test the road. They check thickness, smoothness, and drainage. If all is good, the road is opened to traffic.
Sometimes, toll booths are set up. These collect money for road maintenance.
Challenges in 2025
In India, road construction is slowing down. Only 25–26 km of road is built per day in FY2025–26. This is the lowest in five years. Reasons include long monsoons and fewer new projects.
Still, major roads like the Dwarka Expressway and Mumbai–Nagpur Expressway are progressing. These will improve travel and trade.
For more updates, visit www.rathoreconstruction.org.




good